How to do a good job in logistics system after-sales service | What do you need to know about logistics system after-sales service
After sales service is essential for ensuring the normal operation of the logistics system. The after-sales service capability is considered a key indicator reflecting the comprehensive capabilities of suppliers. Based on over 30 years of professional experience, the author of this article provides a detailed introduction to the content, mode, personnel capability requirements, quality evaluation, and future development trends of logistics system after-sales service.
Introduction: The main content of after-sales service
For logistics systems, after-sales service refers to a series of service work provided by the seller after system handover, aimed at ensuring the sustainable and stable operation of the system throughout its lifecycle. This includes but is not limited to: telephone support, escort, on-site maintenance, fault diagnosis and troubleshooting, training guidance, provision of spare parts, system improvement and optimization, as well as software system bug elimination, data organization, system upgrade, and other work.
After sales service is usually divided into two stages: the first is within the warranty period, which is usually one year, and there are also those that exceed one year, calculated from the system acceptance and launch. The after-sales service during this period is free, or the cost is included in the supply contract. The second stage is the paid service period after the warranty period, which is carried out according to the after-sales service contract signed between the user and the supplier. The commonly understood after-sales service period refers to the second stage.
After sales service is crucial for ensuring the normal operation of the logistics system. In the bidding process of logistics system projects, after-sales service will be a very crucial content, and after-sales service capability is also considered a key indicator reflecting the comprehensive ability of suppliers. Due to the different situations of the user enterprise itself and its logistics system, the after-sales service content that needs to be provided also varies. Some enterprises, especially manufacturing enterprises, have certain mechanical repair and maintenance capabilities, and their demand for after-sales service will be concentrated on key equipment and systems. Daily management and emergency response will be provided by their own teams; Some enterprises, such as some commercial circulation enterprises, do not have corresponding maintenance teams or have weak technical capabilities, resulting in more reliance on after-sales service. However, when there are problems with the logistics system, it is important to be able to quickly resolve them so as not to delay production or reduce the impact of such delays to an acceptable level. When determining a logistics system contract, it is best for user enterprises to include the terms of after-sales service in advance to ensure the normal operation of the system after it is launched.
Once the logistics system is built, it faces after-sales service until the entire lifecycle of the system ends. Generally speaking, the lifecycle of a logistics system is limited by the service life of the equipment, except for extreme examples, it is generally around 20 years. In fact, due to factors such as technological updates, environmental impacts, and changes in business operations, many logistics systems are facing the fate of being dismantled after several years of use, and after-sales service is also coming to an end.

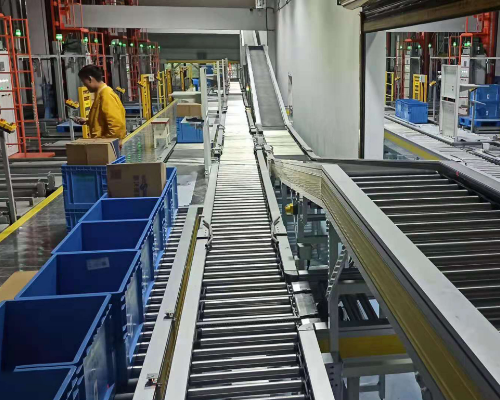
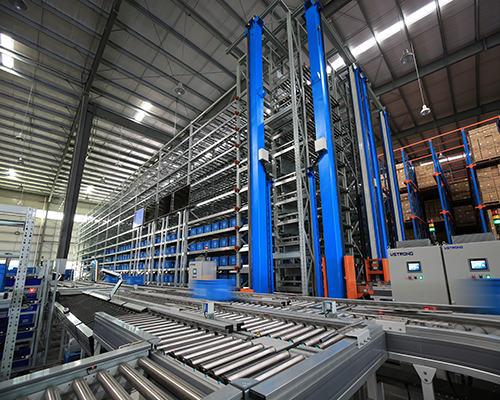
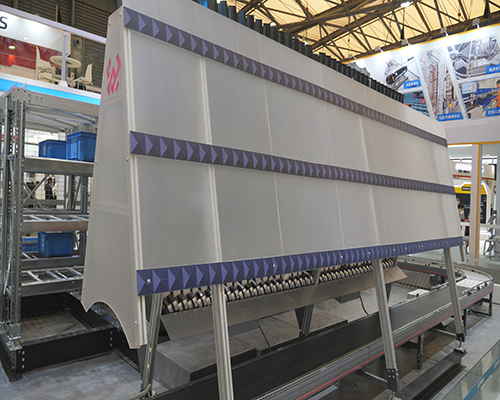
On site maintenance of conveyors
1、 The importance of after-sales service
After sales service is almost a mandatory service for all industrial products. Unlike simple equipment, logistics systems have strong professionalism, involving various specialties, products, and technologies such as machinery, transmission, electronics, sensors, control, computer, network, database, software systems, etc. Some technologies are unique. To solve these problems, only suppliers are generally competent, such as providing computer software, control systems, specialized equipment or technology. Once the logistics system malfunctions during operation, if the supplier cannot provide after-sales service, the system will not be able to ensure normal operation, which will inevitably have a serious impact on production. It can be said that after-sales service is essential for ensuring the normal operation of the logistics system.
After sales service is not only necessary for customer production, but also a supplier's obligation. Fundamentally speaking, all devices and software have the possibility of failure. Even if the logistics system itself is not a problem, external conditions such as power outages and incorrect operations can cause it to malfunction. Moreover, all devices have defects of one kind or another, and all software has bugs. In addition, some parts in the equipment are vulnerable and require timely replacement, which is also a part of after-sales service.
After sales service is still a source of revenue for suppliers. In developed countries such as Europe and Japan, the after-sales service of logistics systems is an important component of their normal business and a stable source of income. According to the maturity of the enterprise, after-sales service generally accounts for 5% to 20% of the enterprise's revenue.
In practical applications, there are indeed many issues where projects cannot provide continuous after-sales service. The reason for this is that some suppliers have issues and are unable to continue providing sufficient after-sales service; Some are users' own problems and have not purchased corresponding after-sales services. Without exception, logistics systems lacking after-sales service will encounter problems, even fatal ones.
Recognizing the importance and necessity of after-sales service is crucial for both suppliers and users. If suppliers cannot provide long-term and effective services, the credit and even survival of the enterprise will be seriously affected; For users, it will be even more devastating, as once suppliers cannot continue to provide services, they will directly face the awkward situation of the system being unusable. At this point, obtaining support from third parties, although it cannot be said to be completely impossible, is very difficult in the current situation because there are very few third-party companies specialized in logistics system maintenance.
2、 Service Model and Its Basic Content
The after-sales service of the logistics system mainly includes: telephone consultation, remote network support (especially for software systems), provision of spare parts, regular maintenance, troubleshooting, daily maintenance services, etc. Some also include system improvement, software upgrades, etc.
From the perspective of suppliers, the after-sales service models of logistics systems are diverse, but generally speaking, they are nothing more than the following:
1. Resident mode
The supplier dispatches after-sales service personnel to provide all after-sales services, including daily use and maintenance, replacement of spare parts, system upgrades, fault handling, etc. Users no longer have or rarely have maintenance personnel. In this mode, the supplier will not only assign special personnel to the site for daily maintenance, but also regularly assign professional personnel to the site for regular inspection and maintenance. This mode is expensive and generally applicable to particularly important systems, such as airport baggage system.
2. General contracting mode
Both parties sign a contract, and the supplier sends technical personnel to maintain the system regularly or irregularly, providing spare parts, etc. The daily management and maintenance are completed by the user themselves. In case of emergency, the supplier shall dispatch maintenance personnel to the site for repair services within the agreed time. This is currently the most common service model. In terms of fees, the standard for software systems is based on the price of the software, usually around 10% to 15%; The hardware equipment is basically maintained at 2% to 3%; Spare parts should be charged based on actual usage, and the specific fees should be determined according to the size of the logistics system.
3. Press mode
Both parties sign a contract to specify the scope of maintenance and fee standards. The supplier will promptly dispatch technical personnel to the site for maintenance according to the needs of the user enterprise. This mode is suitable for a simple and stable system. After a period of operation, the logistics system will enter a stable period with no or few faults, and after-sales service work is relatively less.
4. Other modes
For example, providing escort services at specific times, especially for e-commerce, is very important during the promotion period. Similar situations exist in military and school settings, and users can purchase services specifically for this purpose. For example, when transferring user personnel, it is necessary to provide training for new employees.
It should be pointed out that telephone remote service is the most basic service content and should be included for all modes.

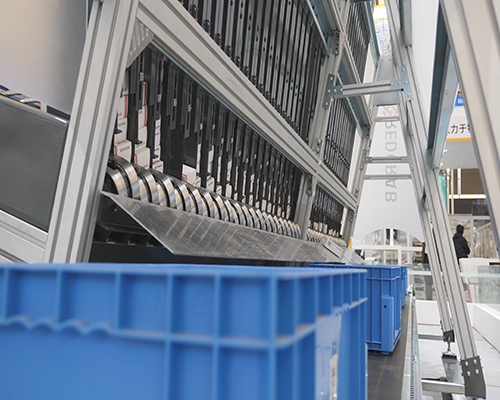
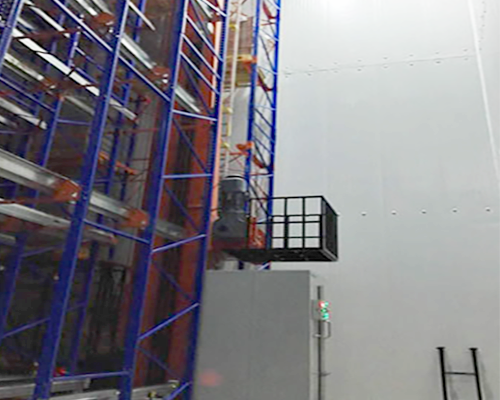
On site maintenance of stacker crane
3、 The abilities that service personnel need to possess
Logistics systems are generally complex, with a variety of equipment types and multiple specialties involved, which puts high demands on after-sales service teams. Generally speaking, for a large-scale logistics system, maintenance personnel should cover multiple specialties, mainly including machinery, control, computer, etc.
Mechanical: This group of personnel requires a college degree or above in mechanical and electrical related fields, with certain experience in mechanical maintenance and repair, and specialized training. Be very familiar with the basic principles and composition of logistics equipment such as stackers, conveyors, sorting machines, elevators, shuttle cars, AGVs, shelves, etc., and have strong hands-on skills. The maintenance of forklifts is generally the responsibility of the forklift factory.
Control: Graduated from a college or above majoring in electrical control, familiar with weak current systems and programmable logic controllers (PLCs), familiar with control principles, and familiar with the working principles of major logistics equipment. Maintenance personnel do not require strong control and programming skills, but they should be familiar with program principles and have the ability to install and run software.
Computer: Graduated from a college or above majoring in computer software, familiar with the working principles and basic functions of WMS and WCS systems, as well as homework processes, familiar with upper level ERP software and lower level control software, and familiar with database operations. Computer maintenance personnel do not need to program themselves, which is the job of software developers. However, they must be familiar with the software environment and operating principles, and have the ability to install and uninstall software.
In addition, maintenance personnel also need to have a certain understanding of electrical and network knowledge.
As a professional service team, logistics system after-sales service also requires service personnel to not only have high knowledge
in mechanical, electrical, control, and computer aspects, but also have special qualification certificates, including electrician
certificates, high-altitude work certificates, and welder certificates. Obviously, many users cannot meet this condition.
Chinese logistics system suppliers all have their own after-sales service teams, and after-sales service personnel are usually transferred from installation personnel to technical personnel. However, Chinese user enterprises generally lack a correct understanding of the value of after-sales service, so there are certain misconceptions about after-sales service, mainly manifested as: they cannot objectively recognize the importance and necessity of after-sales service, and believe that logistics equipment or software systems are perfect and will not malfunction. Therefore, there was no objective consideration for operational and maintenance costs during project initiation, resulting in maintenance costs exceeding the budget range and conflicting with after-sales service fees. Some companies also believe that suppliers should take full responsibility for the failure of logistics systems during operation and implement lifelong free maintenance. However, this is unrealistic and no supplier can achieve this unless this cost is included in the equipment quotation.
4、 Evaluation of service quality
At present, China has not established strict evaluation standards for the quality of after-sales service in logistics systems. Therefore, for the evaluation of after-sales service quality, it is generally based on other industries or products.
1. Punctuality
This mainly includes whether the service can accurately predict before the fault occurs, whether the fault occurs in a timely manner according to the agreement, and whether the fault is eliminated in a timely manner. After sales service has two functions: preventive maintenance and timely troubleshooting. Both are very important. For a logistics system, the highest level is to "treat diseases before they occur", that is, to solve problems before they occur through effective maintenance and upkeep. But some faults cannot be predicted and need to be promptly eliminated after occurrence to reduce losses to an acceptable level.
2. Professionalism
Mainly including whether the personnel have professional literacy, whether the personnel configuration is reasonable, whether the maintenance process and frequency are scientific, and whether the diagnosis of faults is comprehensive and accurate.
3. Effectiveness
It refers to whether maintenance is timely and effective, and truly plays a role in preventing faults. In addition, it also includes whether the spare parts are sufficient, whether the service phone is unobstructed, and whether remote diagnosis can solve the problem.
4. Normativeness
It refers to whether the service process is operated according to the process, such as whether there is an appointment, whether sufficient professional personnel are dispatched, whether the tools are complete, whether the operation process is standardized, whether safety measures are in place, whether acceptance is signed after maintenance is completed, and whether there is a telephone follow-up. Standardization is also an aspect of professionalism.
High quality after-sales service is a reassuring project for users. Active maintenance is to prevent and reduce the occurrence of faults, and emergency response requires fast and effective response. Maintenance personnel should not only possess professional qualities and excellent skills, but also be able to bring benefits to customers. If the service quality cannot meet the requirements or affects the normal production of the user enterprise, this type of service is considered unqualified. Generally speaking, users need to make clear requirements for service quality when signing after-sales service contracts with suppliers.
5、 Future development trends
The after-sales service market for logistics systems in China is huge. Currently, the estimated stock market for logistics systems is around 300 billion to 400 billion yuan. According to the 2% to 3% charging standard, there are approximately 6 billion to 10 billion yuan in maintenance costs annually. Considering the actual situation in our country, only nearly 50% of the systems have signed formal after-sales service contracts. Therefore, the service fee is also around 3 billion to 5 billion yuan. In terms of market growth, there are 80 billion to 100 billion yuan of new logistics equipment added annually, which means an increase of 2 billion to 3 billion yuan. Overall, there are significant market opportunities for after-sales services in China's logistics system.
At present, the main body of after-sales service in China's logistics system is still the supplier. With the increasing scale of the logistics equipment market, especially the deepening of standardization of logistics products, the feasibility of using third-party after-sales services for logistics equipment and systems is increasing, creating conditions for professional logistics system after-sales service companies. The establishment of a professional after-sales service enterprise is expected to provide customers with faster and more professional services, and can also compensate for the shortcomings of inadequate supplier services. From another perspective, it will be a major trend for users to purchase standardized products in the future, which will bring opportunities for the standardization development of logistics products in China.
Similar situations exist abroad. When I visited Japan in 2019, I learned about the complaints of Japanese users about the high after-sales service fees for non-standard equipment. During the communication, they also strongly recognized the importance of using standard products. With the awakening of user awareness, the standardization of logistics systems will become a consensus.
The key to after-sales service in logistics systems lies in prevention and rapid response. From the perspective of technological development trends, the after-sales service of logistics systems will introduce advanced technological means such as artificial intelligence (AI), and use big data, expert systems, etc. to significantly improve the system's fault prevention and warning capabilities and rapid response level. There are already some enterprises both domestically and internationally conducting research and practice. For example, establishing a centralized system testing center, which can quickly determine the health level of the system by monitoring the operating parameters, operating time, environmental noise, electrical load, environmental temperature, and other indicators of on-site equipment through robots. In addition, 5G technology provides infrastructure for remote video diagnosis, remote operation, and remote command, which will greatly facilitate the diagnosis and effective handling of problems, and is expected to significantly reduce after-sales service costs.























 more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more more
more



























